An ERP system has become one of the most important tools for modern manufacturers and distributors. As companies grow, processes become more complex, data becomes harder to control, and disconnected tools slow down productivity. This type of enterprise software creates a single, integrated source of truth that connects inventory, production, warehousing, finance, purchasing, and sales. When implemented correctly, it provides real-time insight, supports decision-making, improves efficiency, and reduces manual work across the operation.
Many organizations begin researching these solutions because their current tools are no longer effective. They may be using accounting systems, spreadsheets, or standalone applications that do not communicate with each other. As operations expand, these limitations cause bottlenecks and unnecessary costs. This guide explains what an ERP system is, how it works, what modules it includes, how it supports manufacturing and warehouse management, and how companies can expand functionality using Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central and solutions from Insight Works.

What Is an ERP System?
An ERP system is Enterprise Resource Planning software that manages and integrates core business processes within a single platform. Instead of storing information across separate tools, the platform centralizes data so that every department works from the same real-time information. This reduces duplication, eliminates manual entry, improves accuracy, and supports better decisions.
Key capabilities include:
• Financial management: general ledger, accounts payable, reporting.
• Inventory management: stock levels, costing, replenishment, forecasting.
• Warehouse management: receiving, put-away, picking, real-time data capture.
• Production management: bills of materials, routings, planning, and scheduling.
• Procurement: vendor information, purchasing workflows, automated replenishment.
• Sales management: orders, pricing, returns, and customer activity.
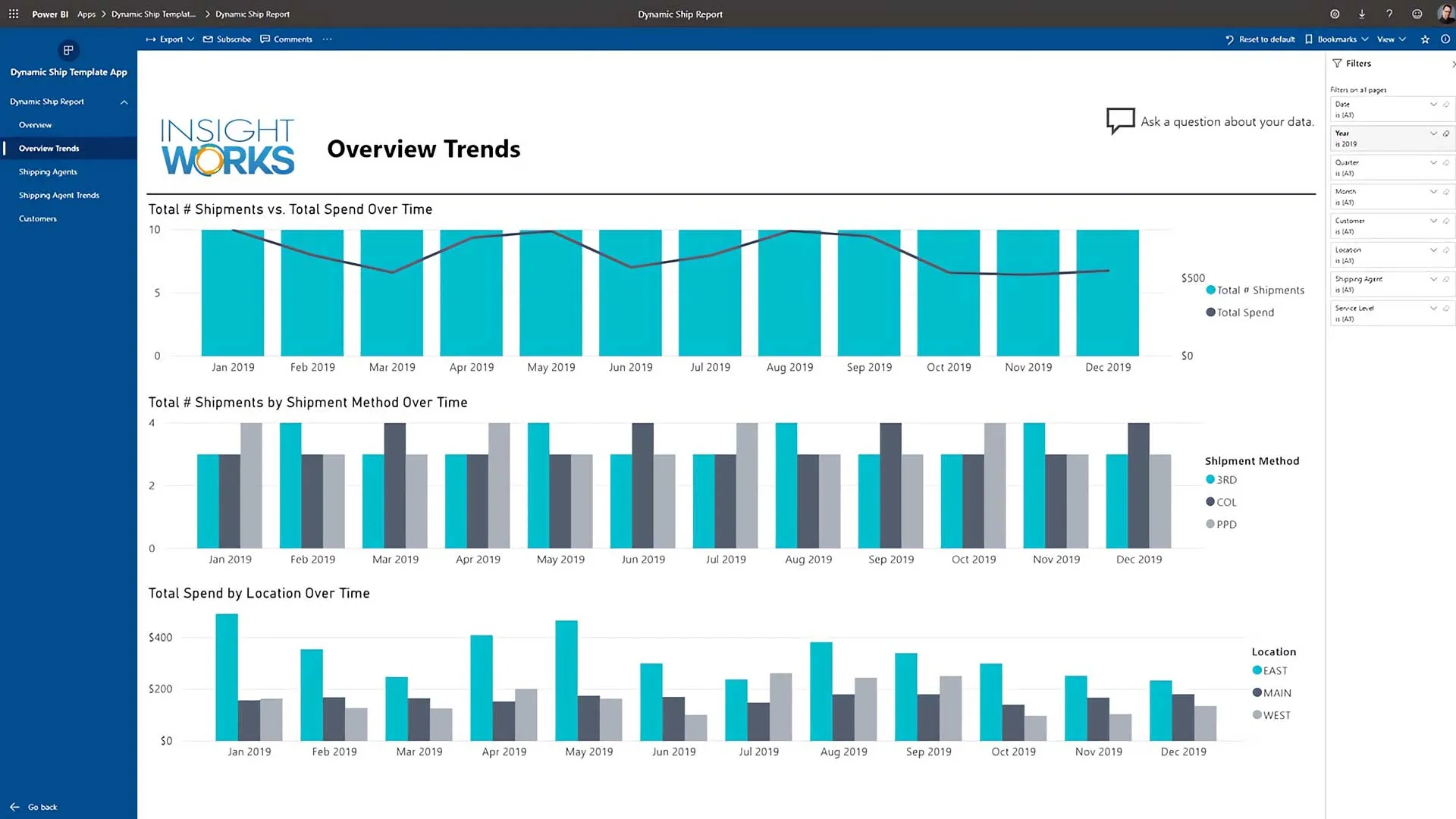
• Reporting and analytics: dashboards and performance insights.
What separates this type of solution from basic accounting systems is the level of integration. When inventory moves, financial data updates automatically. When schedules change, procurement adjusts. When orders are fulfilled, sales and warehouse information aligns immediately. The entire business functions through connected workflows rather than isolated processes.
Modern cloud platforms like Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central are built specifically for small and mid-sized manufacturers and distributors, making this technology accessible and scalable.
How the Platform Supports Manufacturing Operations
Manufacturing requires accurate planning, reliable scheduling, quality control, and efficient use of materials and labor. This software supports these workflows by providing structured processes and real-time feedback.
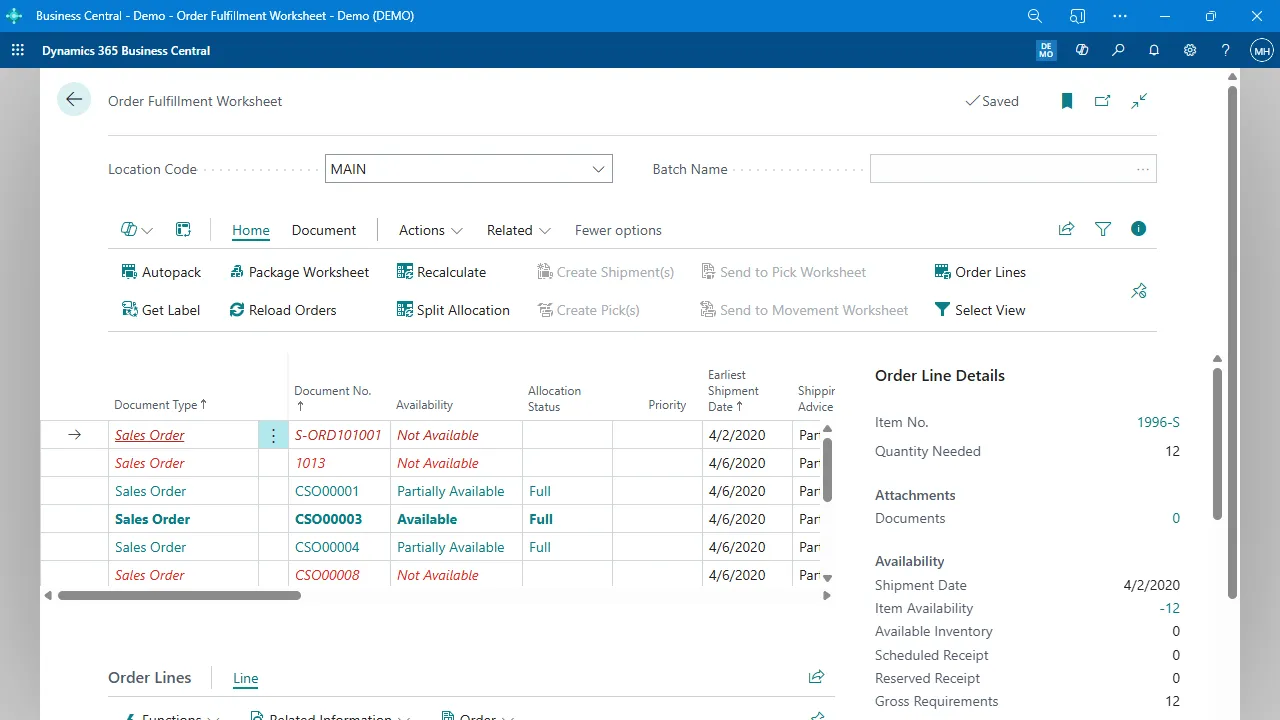
1. Order and demand creation
Customer demand enters through sales orders or forecasts, triggering planning activities such as availability checks and requirement reviews.
2. Bills of materials and routings
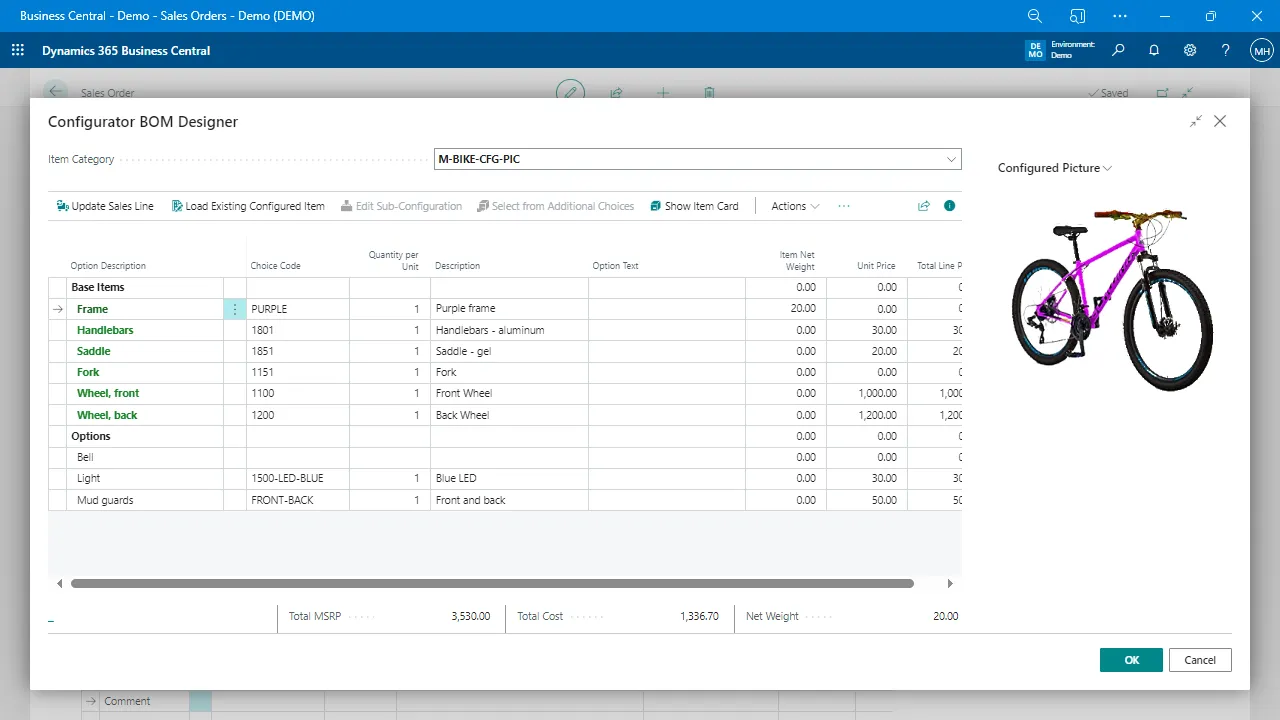
The software stores component lists and production sequences. These define how each product is built and what resources are required.
3. Material planning
The system reviews what components exist, what must be purchased, and when materials are needed. This prevents shortages and helps maintain optimal inventory.
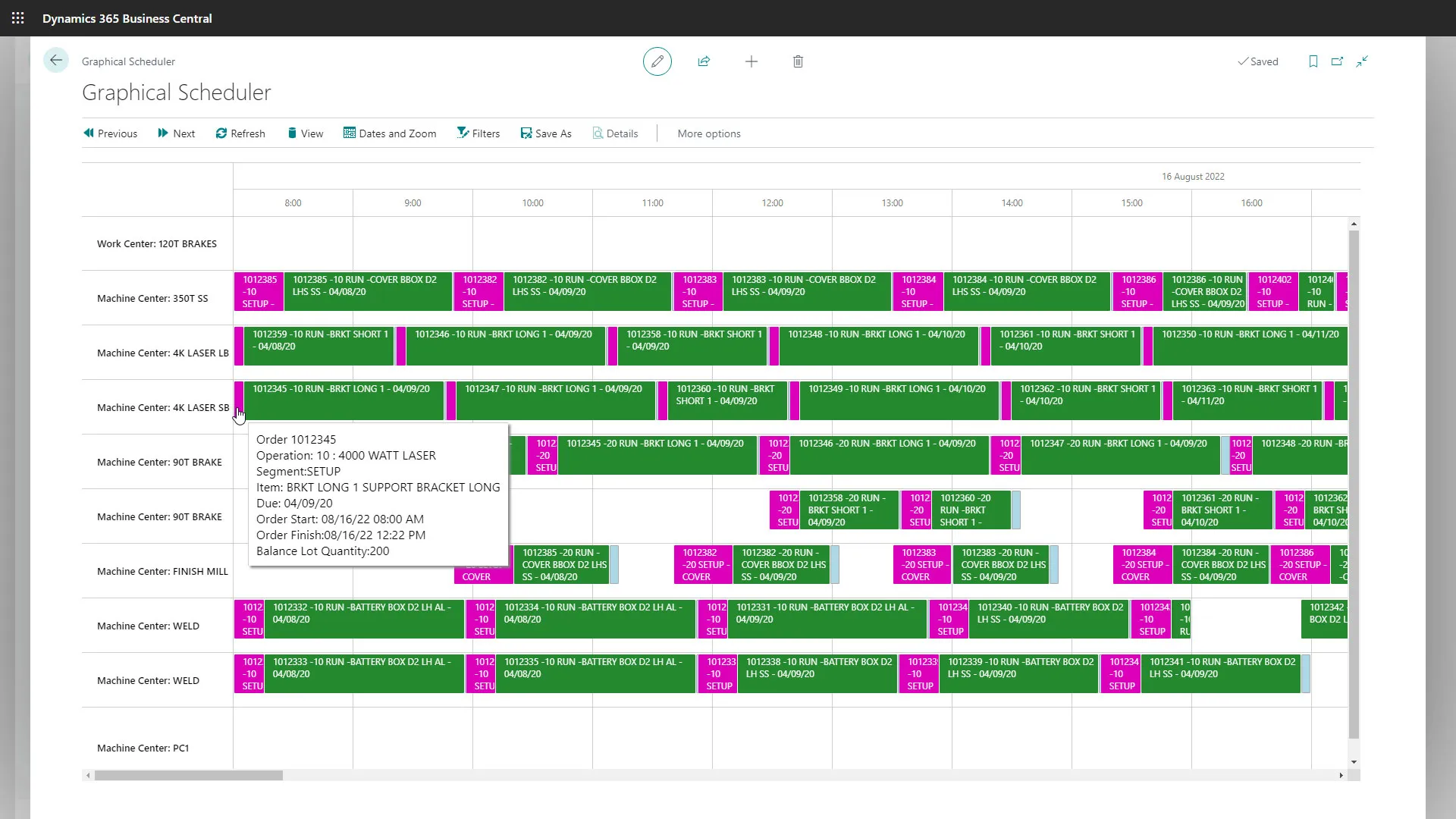
4. Scheduling
Capacity, lead times, and workloads are evaluated. Tools like MxAPS enhance scheduling accuracy for companies using Business Central.
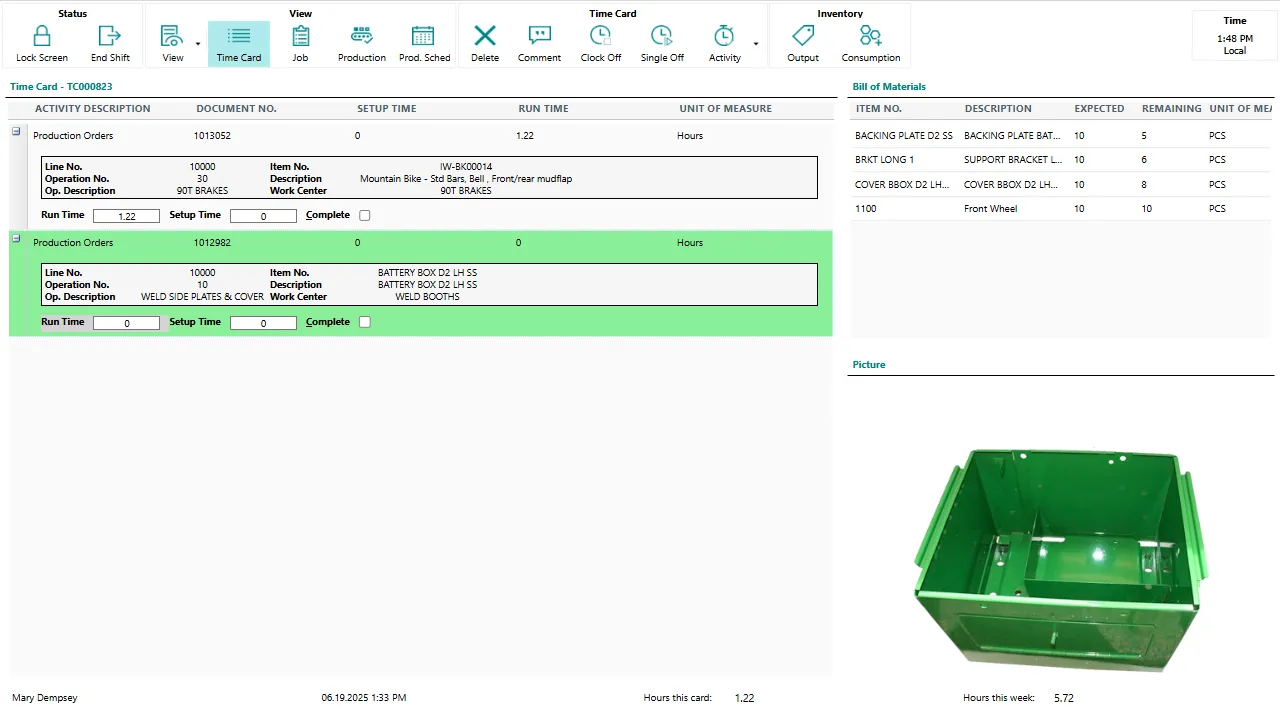
5. Shop floor execution
Operators record output, consumption, and progress. Applications such as Shop Floor Insight automate data collection.
6. Quality and adjustments
Any quality issues or variances are recorded and reflected immediately across the solution.
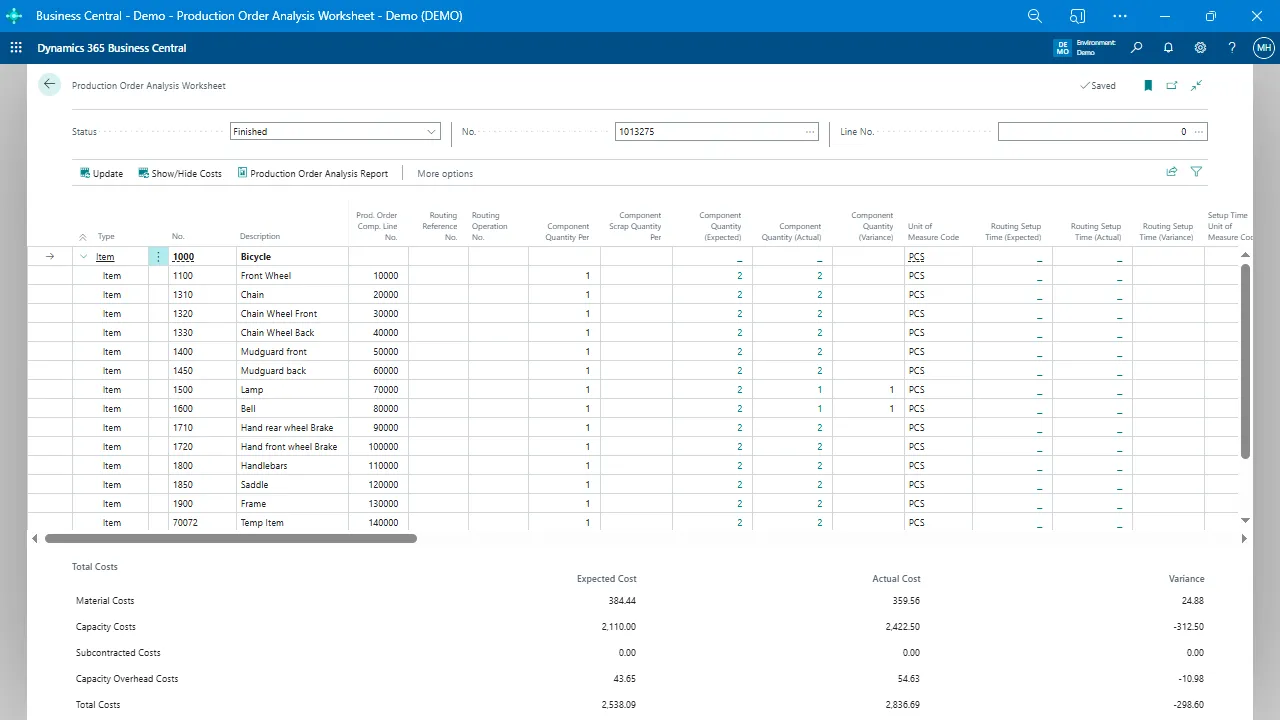
7. Completion and costing
Finished goods update inventory, resource usage is recorded, and costing occurs automatically.
Each step relies on accurate, connected information that flows freely throughout the organization.
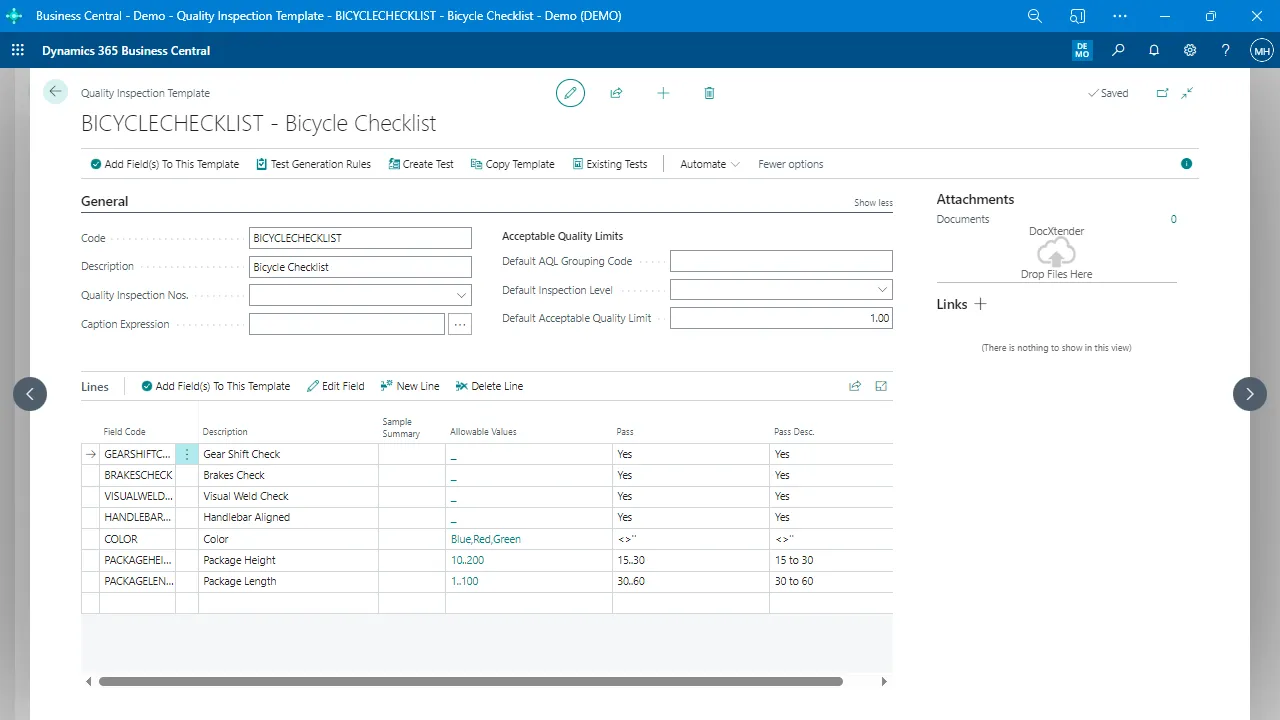
ERP Modules Explained
Enterprise resource planning platforms include several functional areas that manage different parts of the business. When combined, they form a single operational backbone.
Inventory Management
Tracks quantities, item classifications, costing methods, and replenishment logic.
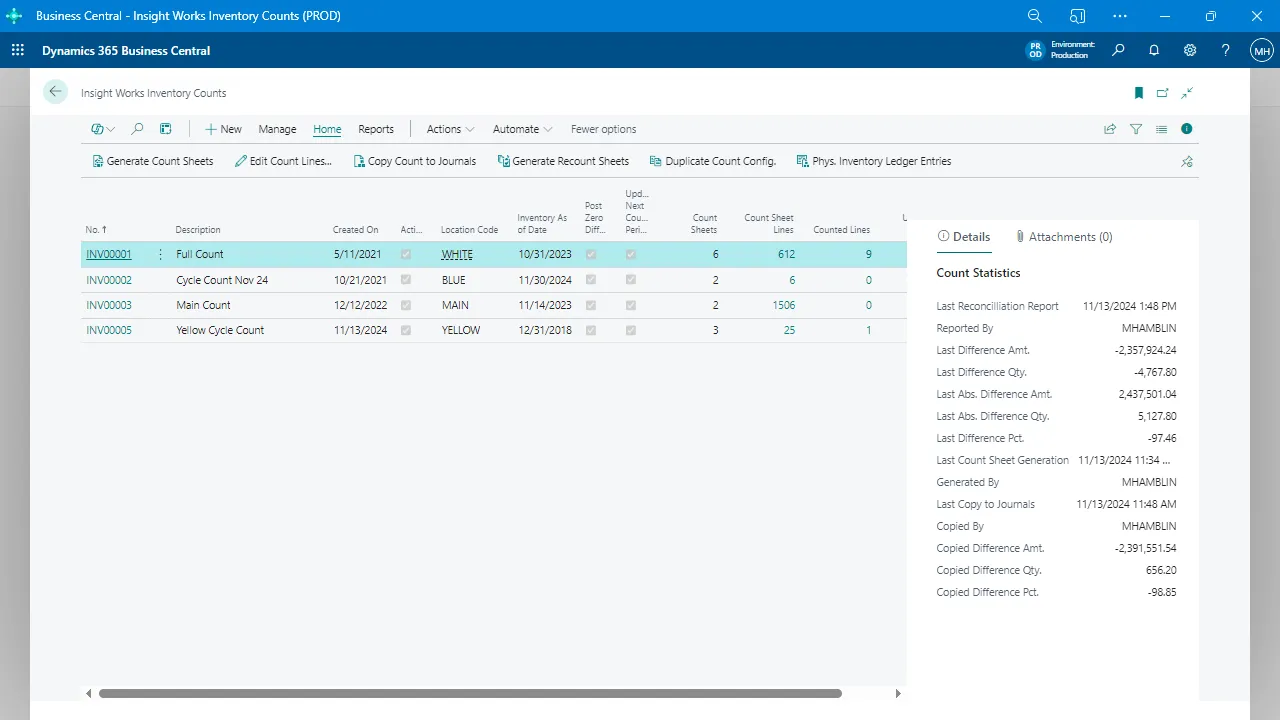
Warehouse Management
Supports inbound and outbound processes, bin management, physical counts, and scanning workflows.
Production Management
Controls bills of materials, routings, production orders, capacity, and scheduling.
Management
Handles budgeting, reporting, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and general ledger activity.
Purchasing
Automates replenishment, vendor communications, pricing, and purchase order processing.
Sales
Manages order entry, customer history, pricing, and fulfillment visibility.
Reporting
Finished goods update inventory, resource usage is recorded, and costing occurs automatically.
Each step relies on accurate, connected information that flows freely throughout the organization.
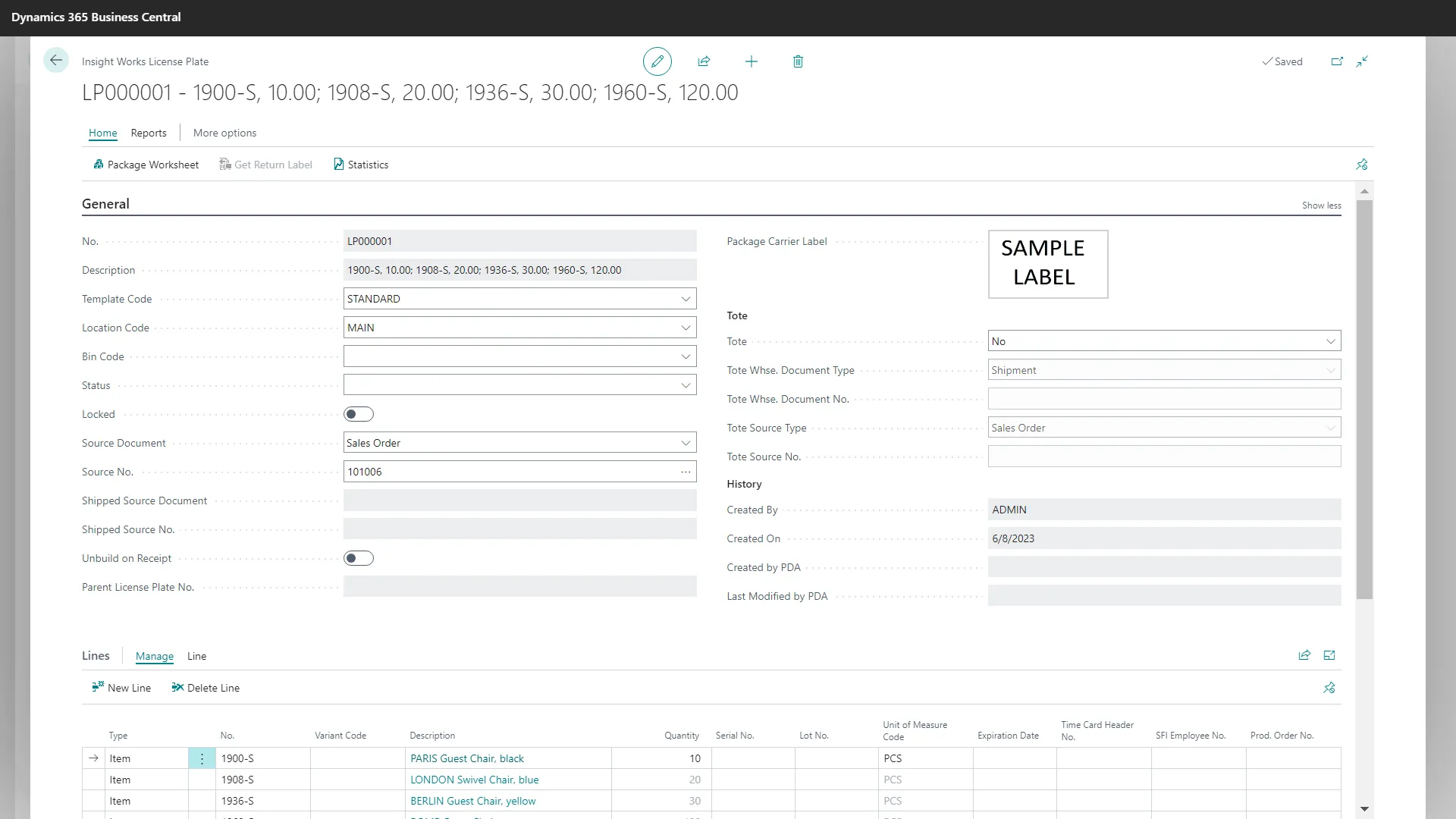
Warehouse Operations and the Role of ERP Systems
Warehousing requires accuracy, speed, and consistency. Many teams rely on manual entry, spreadsheets, or paper-based workflows, which increase the likelihood of errors.
An integrated business platform improves warehouse performance by supporting:
• Receiving and put-away workflows
• Accurate picking
• Real-time scanning
• Bin and storage optimization
• Faster cycle counting
• Improved order fulfillment accuracy
• Better visibility across inbound and outbound activity
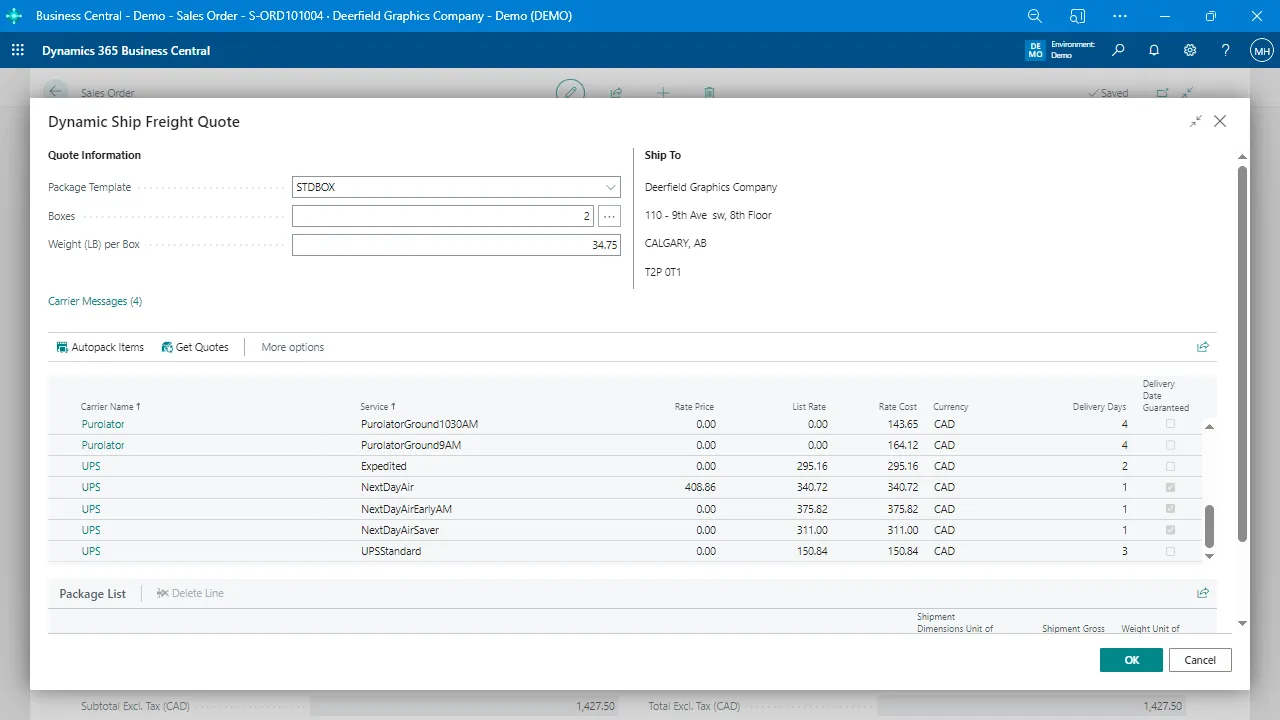
Solutions like Warehouse Insight and WMS Express extend Business Central to provide advanced scanning and device integration, allowing warehouse workers to interact with the system in real time.

Cloud ERP vs On-Prem ERP
Organizations evaluating new software often compare cloud and on-premises deployment models.
Cloud
Hosted online and maintained by the provider. Requires no physical servers and receives ongoing updates. Supports remote access and scales easily.
On-Premises
Installed on local servers and maintained internally. Offers more control but requires more IT resources.
Summary of differences
• Cloud systems scale quickly.
• On-prem requires more maintenance.
• Cloud receives continuous updates.
• On-prem upgrades must be planned manually.
Most small and mid-sized companies choose cloud deployment due to lower overall cost and improved flexibility.
Why Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Is a Leading ERP System
Business Central is one of the most widely adopted ERP solutions for manufacturers and distributors that want a modern, flexible platform. It includes comprehensive modules for finance, inventory, warehousing, production, purchasing, and sales. It supports full manufacturing workflows with bills of materials, routings, capacity management, and planning tools.
Its strengths include:
• Scalability for growth
• Integration with Microsoft 365 and Power Platform
• Cloud reliability and security
• Modern interface
• Large global partner network
• Ability to extend functionality through AppSource
Microsoft’s ongoing investment ensures Business Central evolves continuously with new features and improvements.

How Insight Works Extends Business Central
Insight Works provides specialized solutions that enhance Business Central for manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution. These applications integrate directly and support advanced operational requirements.
Steps to Implement an ERP Solution
A successful implementation requires coordination, preparation, and ongoing support.
1. Discovery
Document processes, identify challenges, and define goals.
2. Process Mapping
Compare current processes to the capabilities of the software.
3. Data Preparation
Clean and validate data before import.
4. Configuration
Set up modules, permissions, workflows, and business rules.
5. Testing
Validate processes and correct issues.
6. Training
Ensure users understand how to operate the system effectively.
7. Go-Live
Transition to the platform with close support.
8. Continuous Improvement
Refine processes, adopt new features, and integrate additional tools.
Each step relies on accurate, connected information that flows freely throughout the organization.
Cost Drivers
ERP investment depends on several contributing factors.
Licensing
Subscription fees for cloud users and functionality.
Implementation
Configuration, training, testing, and process mapping.
Hardware
Unique workflows may require additional development.
Support
Ongoing assistance ensures long-term success.
Understanding cost categories helps organizations plan effectively.
Real-World Scenarios
Improved Production Visibility
Manufacturers gain accurate data that improves scheduling and reduces delays.
Warehouse Automation
Barcode scanning eliminates manual entry and improves accuracy.
Fewer Stockouts
Better forecasting and planning prevent material shortages.
Faster Shipping
Integrated shipping workflows reduce time and improve accuracy.

Understanding cost categories helps organizations plan effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Scanners, tablets, time clocks, and other devices can connect directly.
Manufacturing, distribution, warehousing, and service sectors.
ERP manages the entire business. MRP focuses on materials and production.
When manual work, disconnected systems, or errors begin to slow growth.
Conclusion
An ERP system brings structure, visibility, and efficiency to manufacturing and warehouse operations. It connects departments, reduces manual effort, and provides real-time insight to support better decisions. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a leading option for small and mid-sized organizations that need a modern, flexible platform.
When extended with Insight Works solutions, Business Central becomes a complete operational system that supports scanning, scheduling, shop floor reporting, and shipping. Companies evaluating these solutions can use this guide to understand what an ERP system is, how it works, and how to prepare for a successful implementation.
Understanding cost categories helps organizations plan effectively.
About Insight Works
Insight Works is a global Independent Software Vendor specializing in manufacturing and distribution applications for Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central. With 800+ global partners and 50,000+ AppSource installations, Insight Works is one of the most widely adopted solution providers in the Business Central ecosystem.